Description
Depression Detection Using Advanced Graphical Deep Learning – Part 3 (Features Extraction)
Introduction
Electroencephalography (EEG) is widely utilized in clinical settings for disease diagnosis due to its high temporal resolution, non-invasiveness, and inexpensive data gathering costs. Research in psychological and cognitive sciences has demonstrated that EEG signals can effectively reflect the majority of psychological and cognitive functioning. Prior research has utilized approaches such as dimensionality reduction or extraction of frequency band signals as pre-processing steps to obtain features. These features are then used with machine learning algorithms as classifiers to carry out certain tasks. Nevertheless, the efficacy of these approaches is highly dependent on the precision of the chosen features, and there is no connection between the classifier and the pre-extracted features.
Among the various approaches utilized, the employed deep learning techniques can be roughly classified into two categories: CNN-based (Convolutional Neural Network) and GNN-based (Graph Neural Network). CNN-based algorithms treat EEG data as images and utilize convolutional kernels to extract features. However, they do not fully take into account the interplay between multiple channels. Conversely, techniques based on Graph Neural Networks (GNN) convert EEG signals into data with a graph structure. These algorithms utilize pre-computed adjacency matrices to represent the connections between different channels. These approaches consider the overall spatial structural linkages between different channels, making it easier to extract features that are connected across channels.
The EEG signal, being a natural high-resolution data, possesses a temporal dimension. Multiple studies are consistently investigating the temporal correlation in the EEG signal, which is utilized for tasks such as emotion recognition and disease diagnosis, and have obtained satisfactory outcomes. Prior studies can be broadly categorized into two groups: models including stacked time series modules and time series hybrid models. The model incorporating a stacked time series module has the capability to extract the temporal relationship in features by incorporating separate timing modules in the processing flow.
Time series hybrid models use numerous network structures to create a new hybrid model that extracts characteristics from multiple dimensions by integrating the time series model structure with other network structures. The GRU-Conv hybrid deep learning model, which combines the GRU and CNN architectures, is designed to extract sleep categorization features and demonstrate high performance on the SEED and DEA datasets. The ST-GCLSTM model has a spatial graph convolutional network module and an attention-enhanced bidirectional LSTM module. These modules are designed to extract important spatiotemporal properties from continuous EEG signal data in order to recognize emotions.
Challenges
While previous research has shown promising outcomes in several EEG activities, it is not feasible to directly utilize these findings for detecting Major Depressive Disorder (MDD) using EEG data. Our research is currently focused on the difficulty of integrating spatial structure and temporal dependence information in individuals with depression who have varied brain networks.
Requirement
Identifying and enriching spatiotemporal features from the EEG is also very important in the research paper because it determines how activity in the brain progresses in space and time. Thus, by obtaining spatial information at various electrodes and temporal dynamics over time, the model acquires a global perspective of the brain’s activity especially in tasks such as emotion detection and disease diagnosis. The fact that the model includes spatial graph convolutional networks and bidirectional LSTM modules allows extracting important spatial and temporal features from continuous EEG data. This approach guarantees that the model can capture spatial and temporal properties, including temporal dependencies, which is critical in identifying patterns concerning the brain’s activity linked to depression. Explaining the aspects of spatiotemporal features extraction: timing relationships in features could be viewed as timing graph, serialized features could be viewed as features over time. Therefore, transformation of EEG signals into spatiotemporal features is crucial because when transforming multi-channel EEG data into time series, spatial and temporal aspects of brain activity can be investigated jointly, which is previously impossible, and improve the efficiency of the model’s ability to diagnose such conditions as depression.
Process
The model’s general framework has three steps. Initially, we investigate the brain’s network connection status as indicated by EEG and compute the adjacency matrix. Next, we employ multi-layer Graph Convolutional Networks (GCNs) and Gated Recurrent Units (GRUs) to integrate many dimensions of input. This allows us to investigate the spatial relationship between distinct channels and the temporal connection of changes in the brain network. Ultimately, we calculate the significance of each node by analyzing the structure of the graph, and we keep the nodes that are most indicative for forecasting sadness.
Diagnosing depression using Graph Neural Networks (GNN) usually requires pre-computing the adjacency matrix, which fails to consider the differences in brain network connection between individuals with depression and those who are mentally well. In order to address this problem, we suggest the implementation of an Adaptive Graph Topology Generation (AGTG) module. This module would create the topological connections of a graph by analyzing EEG signals in a flexible manner, namely through the generation of an adjacency matrix. The objective of our approach is to achieve enhanced connection that is both adaptable and accurate by including geographic distance and correlations among various channels.
The GCGRU module integrates the Graph Convolutional Network (GCN) structure and the Gated Recurrent Unit (GRU) structure to extract spatiotemporal features from the graph structure generated by the Attention-guided Temporal Graph (AGTG) module. This allows for capturing the dynamic changes in brain network connection. More precisely, we divide each EEG sample into a sequence of EEG sub-slices of a predetermined length. Next, we employ the AGTG module to produce a graph adjacency matrix for each sub-slice, where the original time-domain data serves as the node characteristics of the graph. Ultimately, the EEG sample was converted into a sequence of graphs, and we employ various GCGRU models to capture the spatial and temporal dependency characteristics.
In order to enhance the model’s ability to extract features, we propose the incorporation of residual networks and the implementation of a cross-layer concatenation operation within the numerous levels of GCGRU. This allows for the merging of outputs from various layers.
Code Description
The code given in Figure 1 implements a Graph Convolutional Network (GCN) layer. It’s built-in as a subclass of nn.Module, the GCN_Layer class for the neural network layer of the graph. To do that, the module defines the W matrix of size input_dim by output_dim with Xavier uniform errors. The forward method takes an input feature matrix x and an adjacency matrix, and calculates the matrix multiplication, which includes the adjacency matrix, the input features, and the weight matrix (AXW). Subsequently applied on that, there is a rectifying activation function known as ReLU, and afterwards there comes dropout with dropout_prob probability before it gives the final output. This way, when boosting the characteristics, the process occurs by way of adjacency matrix and does not take much time.

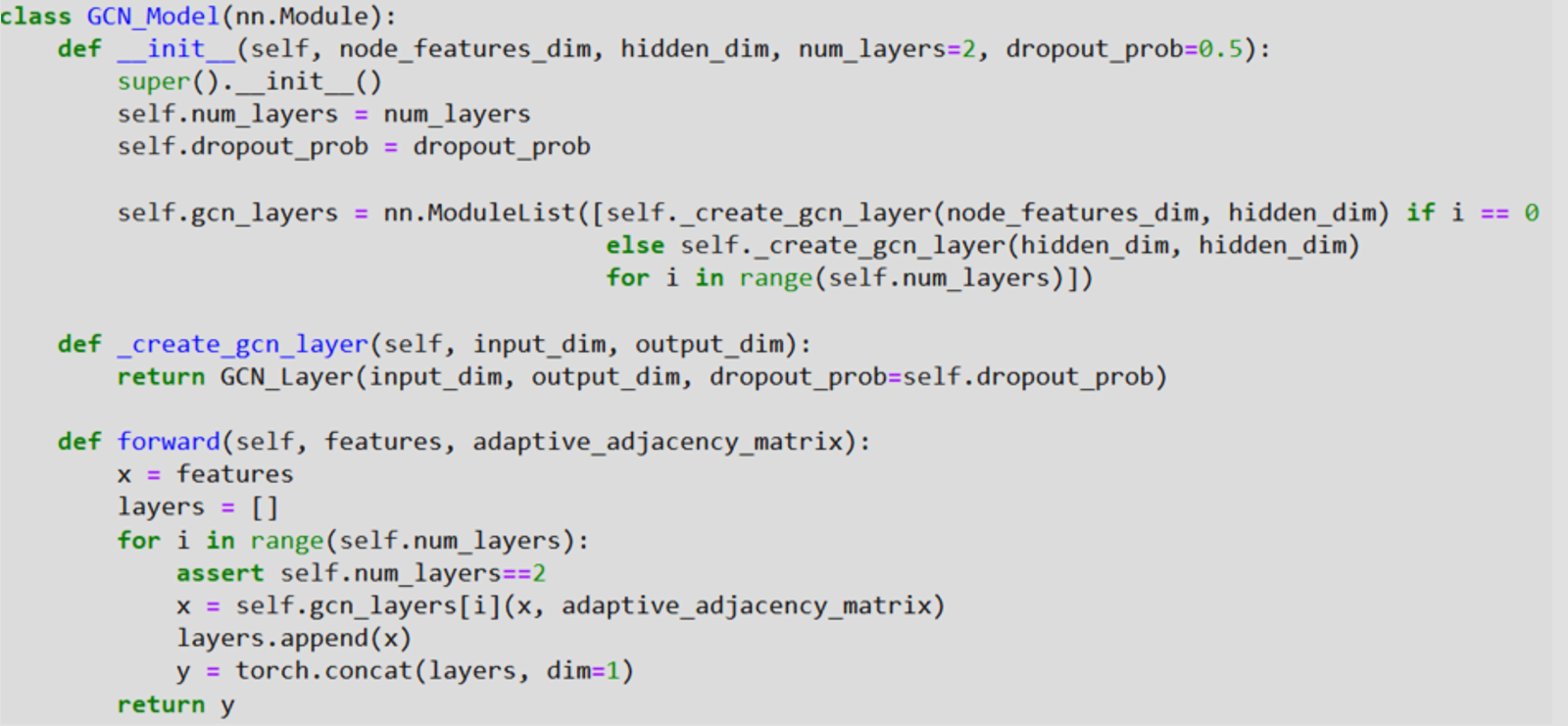
A GCN model is illustrated in Figure 2 trained under the PyTorch environment. The GCN_Model class is designed to build graph convolutional neural networks since it is a subclass of the nn package. Module and it forms a list, the gcn_layers has dimensions as node_features_dim and hidden_dim while initialization. The create_gcn_layer function is used to create each of the GCN layers. The forward technique feeds the input features as well as an adjustable adjacency matrix through a series of GCN layers step by step. The given layer’s outcome is stored in the layers list for the next layer to reuse if required in its operation. Finally, after passing through all the layers, the final output is computed by sum product along a dimension of 1 of all the layers.
However, a Gated Recurrent Unit (GRU) cell is described in Figure 3 below. The GRU_Cell class is a subclass of nn.Module, it is a recurrent neural network cell that operates in both the forward and the backward direction. This defines the weight matrices and bias vectors for the reset gate (Wr_x, Wr_h, br), the update gate (Wu_x, Wu_h, bu), as well as the candidate hidden state (Wc_x, Wc_h, bc). To implement the forward method, one needs to input feature vector at current time t_0 and a hidden state of time t_1. The reset gate r_t_0, the update gate u_t_0 besides the candidate concealed state c_t_0 gets computed using sigmoid or tanh activation function. Finally, it determines the concealed state at time t_0 through a first-order linear interpolation of the previous concealed state and the possible concealed state, controlled by the update gate.

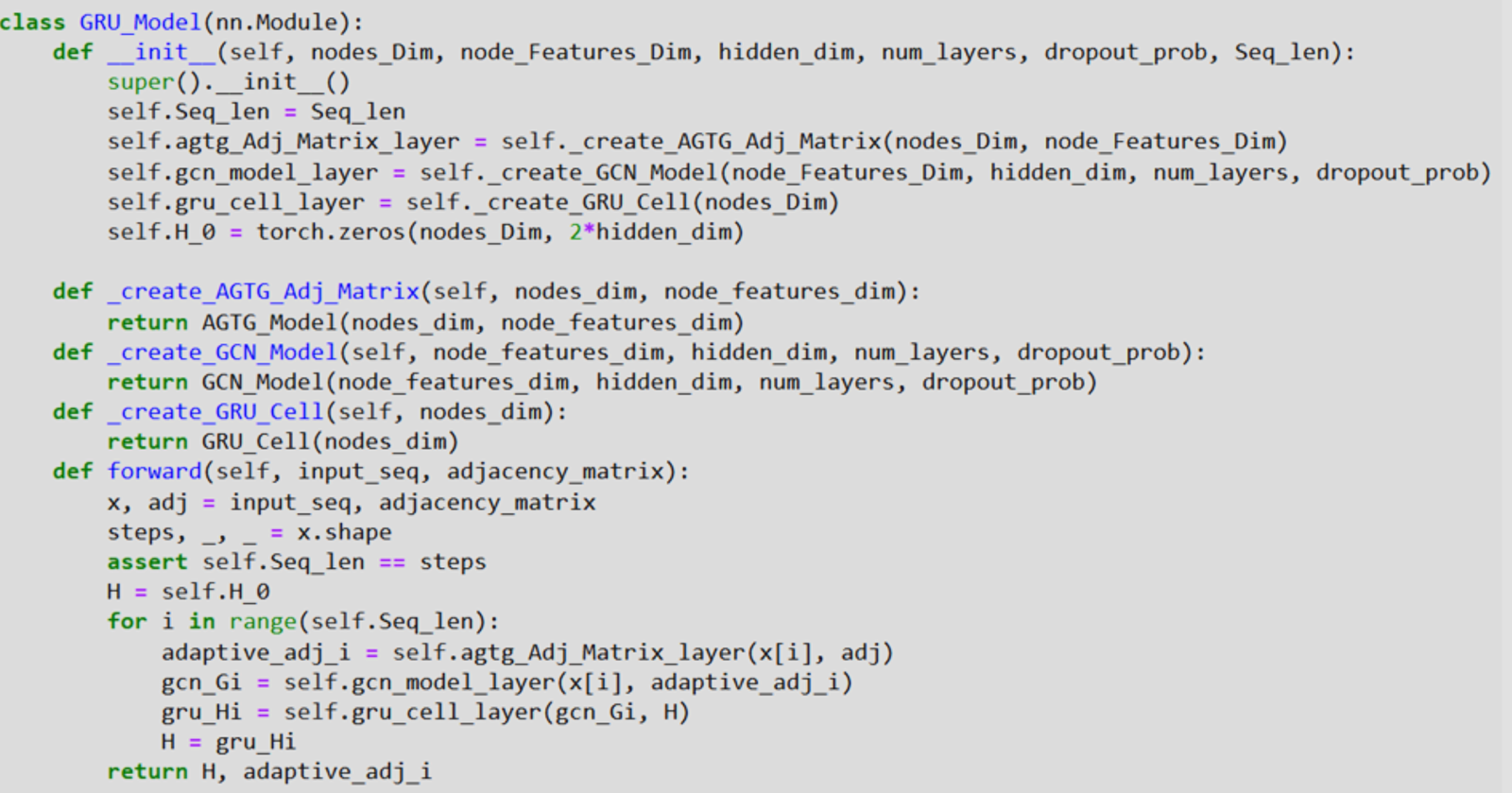
Next, in Figure 4, the Gated Recurrent Unit (GRU) architecture is described to operate data with graph topology. The GRU_Model class is a class which becomes a subclass of nn.Module and it initializes many layers: a first adjacency matrix layer as part of the AGTG model, a GCN model layer, a GRU cell layer and H_0, the first hidden state which is set to zero. The forward method requires as input an input sequence and a matrix of adjacency. In the case of using the AGTG layer for every time step of the sequence, it determines an adaptive adjacency matrix. It then feeds the input features and the learnable adaptive adjacency matrix to the GCN model to get an embedding in the graph structure. Lastly, it determines the new hidden state through the GRU cell. Thus, the output is made of the final hidden state and the final adaptive adjacency matrix.
References
Zhang, Z., Meng, Q., Jin, L., Wang, H., & Hou, H. (2024). A novel EEG-based graph convolution network for depression detection: incorporating secondary subject partitioning and attention mechanism. Expert Systems with Applications, 239, 122356.
Wang, H. G., Meng, Q. H., Jin, L. C., & Hou, H. R. (2023). AMGCN-L: an adaptive multi-time-window graph convolutional network with long-short-term memory for depression detection. Journal of Neural Engineering, 20(5), 056038.
Garg, S., Shukla, U. P., & Cenkeramaddi, L. R. (2023). Detection of Depression Using Weighted Spectral Graph Clustering With EEG Biomarkers. IEEE Access, 11, 57880-57894.
Ning, Z., Hu, H., Yi, L., Qie, Z., Tolba, A., & Wang, X. (2024). A Depression Detection Auxiliary Decision System Based On Multi-Modal Feature-Level Fusion of EEG and Speech. IEEE Transactions on Consumer Electronics.
Other Related Product Links
[Python Code for Depression Detection Using Advanced Graphical Deep Learning – Part 2 (Adjacency Matrix Generation)] (https://scholarscolab.com/product/eeg-sensors-relational-analysis-and-adjacency-matrix-generation/)
[Python Code for Depression Detection Using Advanced Graphical Deep Learning – Part 4 (Graph Topology)] (https://scholarscolab.com/product/graph-topology%e2%80%90based-depression-detection//)

abhishek gupta
ScholarsColab.com is an innovative and first of its kind platform created by Vidhilekha Soft Solutions Pvt Ltd, a Startup recognized by the Department For Promotion Of Industry And Internal Trade, Ministry of Commerce and Industry, Government of India recognised innovative research startup.






































mr.mi –
good
raja.gopal (verified owner) –
NA
karthik.p (verified owner) –
This will be useful for my UG students to work on the ideas
karthik.p (verified owner) –
yes
karthik.p (verified owner) –
good
karthik.p (verified owner) –
Good
farha jabin.oyshee (verified owner) –
good
abdul.fofanah (verified owner) –
This is good start to development of research